INTRODUCTION
The failure of classical mechanics led Planck(in 1900) to the discovery that radiation is emitted in quanta whose energy is E=hν. In 1901, Planck was able to derive an empirical formula to explain the experimentally observed distribution of energy in the spectrum of a black body, on the basis of his revolutionary hypothesis known as quantum theory of heat radiation. This was the Origin of quantum Mechanics(click here) |
| Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck |
This realtion agrees (and hence completely fit) with the experimental curves obtained. This formula of distribution of energy with wavelengths, on the basis of his quantum concept, was deduced using following assumptions, which may be called as Planck's quantum postulates.
PLANCK'S QUANTUM POSTULATES
1) A black body contains the atomic oscillators capable of vibrating with all possible frequencies. An oscillator of frequency ν can not have any energy but only discrete values of energy given by
E(n) = nhν ----(1)
where n= 0,1,2,3,4,.....
ν= oscillator frequency
h= Planck's constant
2) The atomic oscillator can not emit or absorb energy continuously. But it can emit or absorbs the energy in discrete units of energy, a tiny packet called 'quanta'. The quantum energy is due to jump of the oscillator from one energy level to the other and is given by
ΔE(n) = Δn(hν).
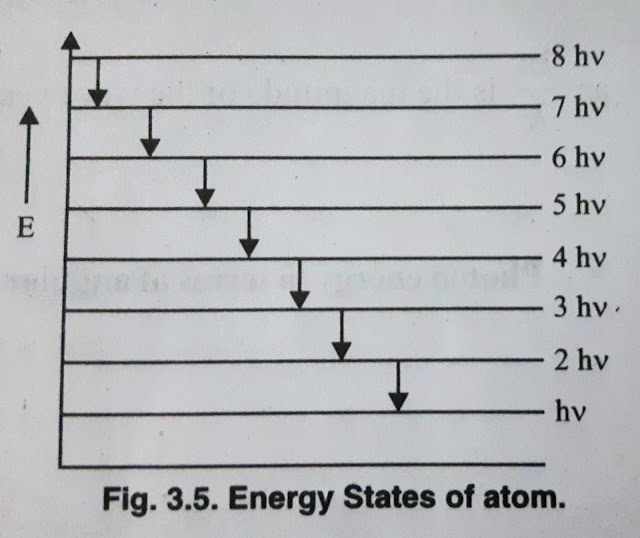
where Δn = difference of levels. For example, if the transition energy levels are n=8 and n=5, then
ΔE= E(8) - E(5) = 8hν - 5hν = 3hν
The matter can emit or absorb the radiation i.e. quantum of energy by jumping from one energy state to other.
The oscillator emits energy only when it passes from a higher energy state to a lower energy state and absorbs energy when it goes from a lower energy state to a higer energy state. No emission or absorption of energy takes place when the oscillator is in a given state.
The smallest amount of energy which can be emitted or absorbed by the oscillator is hν.
In other words a radiation of frequency ν is emitted as quantum of energy E= hν where h is Planck's universal constant having a value equal to
6.62607015 × 10−34 joule second. The quantum is the basic unit of energy and cannot be subdivided. It is the quantum of energy and Einstein named it as a photon.
What is a photon? Photon is a particle of zero rest mass. Its dynamical variables are energy(hν) and momentum(h/λ). A photon has zero charge and spin equal to one quantum unit. Two charges or two magnetic poles exert a force on each other due to exchange of photons. A photon interacts with all the charged particles and can interact with some neutral particles.
A photon behaves as a small elastic sphere for all purposes. When a photon collides with an electron both momentum and energy are conserved as in the case of collision between two elastic spheres. This fact has been verified by Compton in his experiments on X-Rays(click here to know more)
For derivation of Planck's energy distribution formula visit-Planck radiation law.
This theory has been able to explain a number of phenomena which could not be explained according to the classical conception of radiation. For example, it gives a very satisfactory explanation of variation of specific heat of solids with temperature, Photo-electric Effect, Compton Effect etc. and has been successfully applied by Bohr in the theory of the hydrogen spectrum.
NEXT BLOG - Black body radiation.
Click on the sidemenu and follow the blog!
Click on subscribe button for email subscription.
Share your feedback down in the comment box.
Thanks for reading!
Our facebook page- Knowfhysics Facebook page
Our Quora space - Knowfhysics quora space
2) The atomic oscillator can not emit or absorb energy continuously. But it can emit or absorbs the energy in discrete units of energy, a tiny packet called 'quanta'. The quantum energy is due to jump of the oscillator from one energy level to the other and is given by
ΔE(n) = Δn(hν).
where Δn = difference of levels. For example, if the transition energy levels are n=8 and n=5, then
ΔE= E(8) - E(5) = 8hν - 5hν = 3hν
EXPLANATION
From the first assumption, given by equation (1) it is clear that each quantum of energy depends upon the frequency of radiation(ν) and is not divisible. Moreover, the exchange of energy between matter and radiation is in terms of integral multiple of hν. Therefore, the total energy exchanged may be 0, hν, 2hν, 3hν,......., nhν in discrete manner.
However, according to classical theory, the atom can possess any amount of energy from zero to infinity, hence exchange of energies are continuous i.e. from 0 to infinity which is inadequate to quantum concept.
According to Planck's theory, the atom is associated with the allowed energy states called quantum states and its energies are quantized.
The matter can emit or absorb the radiation i.e. quantum of energy by jumping from one energy state to other.
The smallest amount of energy which can be emitted or absorbed by the oscillator is hν.
In other words a radiation of frequency ν is emitted as quantum of energy E= hν where h is Planck's universal constant having a value equal to
6.62607015 × 10−34 joule second. The quantum is the basic unit of energy and cannot be subdivided. It is the quantum of energy and Einstein named it as a photon.
What is a photon? Photon is a particle of zero rest mass. Its dynamical variables are energy(hν) and momentum(h/λ). A photon has zero charge and spin equal to one quantum unit. Two charges or two magnetic poles exert a force on each other due to exchange of photons. A photon interacts with all the charged particles and can interact with some neutral particles.
A photon behaves as a small elastic sphere for all purposes. When a photon collides with an electron both momentum and energy are conserved as in the case of collision between two elastic spheres. This fact has been verified by Compton in his experiments on X-Rays(click here to know more)
For derivation of Planck's energy distribution formula visit-Planck radiation law.
This theory has been able to explain a number of phenomena which could not be explained according to the classical conception of radiation. For example, it gives a very satisfactory explanation of variation of specific heat of solids with temperature, Photo-electric Effect, Compton Effect etc. and has been successfully applied by Bohr in the theory of the hydrogen spectrum.
NEXT BLOG - Black body radiation.
Click on the sidemenu and follow the blog!
Click on subscribe button for email subscription.
Share your feedback down in the comment box.
Thanks for reading!
Our facebook page- Knowfhysics Facebook page
Our Quora space - Knowfhysics quora space
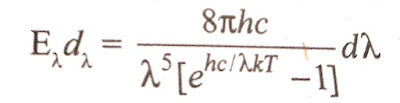

Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or suggestions please kindly share.