Force is the most common term in the classical physics or classical mechanics. The type of force that only occurs when the two surfaces are in physical contact is called as a contact force. One of the example of contact force is friction.
Friction coefficient - Basically it defines the roughness of the surface, i.e. the value of frictional force. The coefficient is dimensionless and unit less.
We can also say that the ratio of frictional force to the normal reaction is called friction coefficient, which in all case is a constant. This constant ratio is called the coefficient of friction and is usually symbolized by the Greek letter mu (μ). Since it is only a ratio of forces , the coefficient is dimensionless.
The value of friction coefficient can also be calculated using tan(theta), because tan(theta) is also the same ratio.
Friction is considered as an electromagnetic force. This is confusing for most of the people to imagine friction as an electromagnetic force, but it is. There are charged particles on both the surfaces. When there is a motion the forces that are exert by the charged particle on each other opposes the relative motion of both the bodies. This force is called as frictional force.
One of the main characteristics of frictional force is that it opposes the relative motion between 2 bodies.
For an example -
Let A and B be the 2 bodies that are in contact and have relative motion. Suppose A is moving more faster than B. So in this case where the friction will act on both the bodies? Be clear that friction wants to oppose relative motion. So frictional force will act in such a way that it will make A to move slowly and B to move fast, so that the relative motion could become zero. In other words friction will deaccelerate A and accelerate B.
Now frictional force can operate between a given pair of solids , a solid and fluid or in given pair of fluids. Frictional force exerted by fluids is called as viscous force. Here we are only talking about solids.
For understanding friction we have to understand few basic terms or definitions, that are as follows-
- Contact Surface- Contact surface is that surface of plane on which both the bodies are in contact.
- Contact Force- Resultant of all the forces exerted by a body on another body due to their contact is called a contact force. Each body exerts it on one another.
- Normal force- The component of the contact force perpendicular to the contact surface or the component of contact force normal to the contact surface is called normal force.
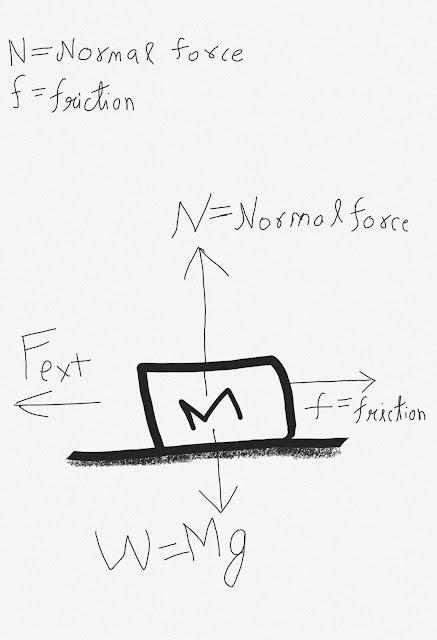
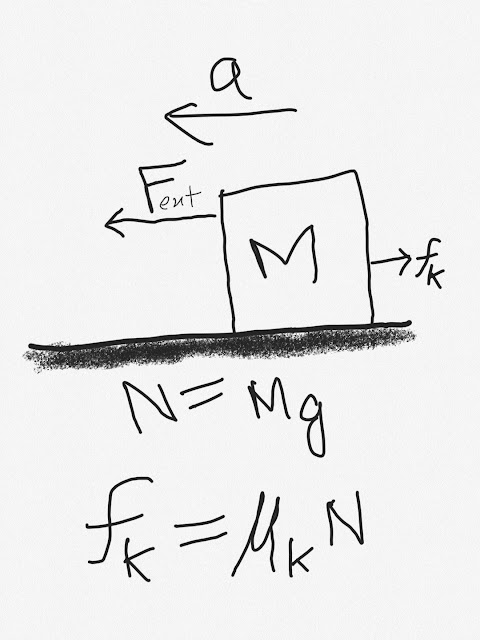
Now suppose that a mass M is kept on ground. The object is at rest. Then an external force F is applied on the obect in the direction shown in the figure. Let f be the frictional force acting on the mass in the direction opposite to the external force.
Let F=f.
Then we can say that the object will be at rest. In this case the forces that operate are- weight, normal reaction, external force, frictional force.
But the forces that are applied by the ground to the mass because of their contact are - frictional force and normal force. Hence for calculating contact force we have to only consider friction and normal reaction.
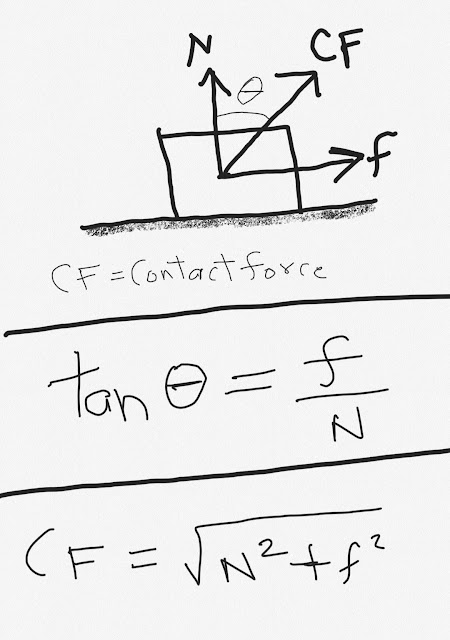
From the above figure, let theta be the angle between normal and contact force. Then tan(theta) will be equal to (f/N). Contact force can also be calculated using the above formula.
Friction coefficient - Basically it defines the roughness of the surface, i.e. the value of frictional force. The coefficient is dimensionless and unit less.
We can also say that the ratio of frictional force to the normal reaction is called friction coefficient, which in all case is a constant. This constant ratio is called the coefficient of friction and is usually symbolized by the Greek letter mu (μ). Since it is only a ratio of forces , the coefficient is dimensionless.
The value of friction coefficient can also be calculated using tan(theta), because tan(theta) is also the same ratio.
Types of friction
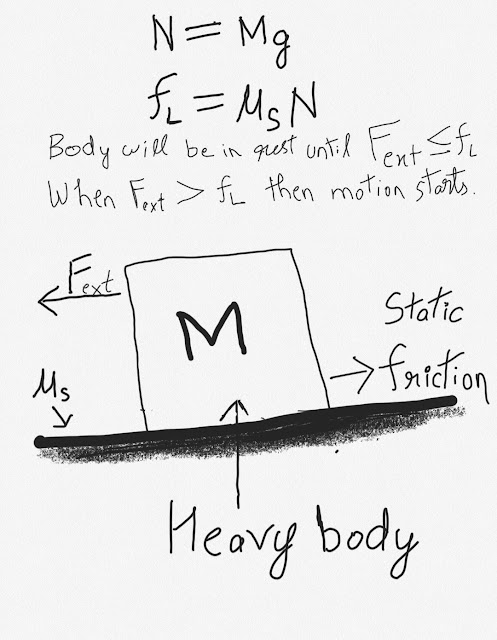
There are two types of friction. When there is no relative motion between two surfaces or when there is no slipping of one body on another then the friction which operates is called as static friction.
Static frictional force can vary from zero to a limiting value F(L). It depends upon the external force that is being operated on the body. If the external force (F) will be less than or equal to the limiting static frictional force then the body will be at rest. But if the external force is more than the limiting friction then the body will start motion. Friction coefficient of static friction is denoted by mu_s (μs).
Static frictional force can vary from zero to a limiting value F(L). It depends upon the external force that is being operated on the body. If the external force (F) will be less than or equal to the limiting static frictional force then the body will be at rest. But if the external force is more than the limiting friction then the body will start motion. Friction coefficient of static friction is denoted by mu_s (μs).
When the body starts slipping on another body or when the relative motion starts, then the friction acting between surfaces is called as kinetic friction. Friction coefficient of kinetic friction is denoted by mu_k (μk). It has a constant value. It does not vary. It is less than static friction. So it becomes easier to move an body after it starts moving.
Friction is an important factor to consider in experiments of classical mechanics. To reduce the friction, lubricants are used. Which reduces the value of friction coefficient of the surface. Only in ideal situations coefficient of friction is considered as zero.
Thanks for reading!
For subscription

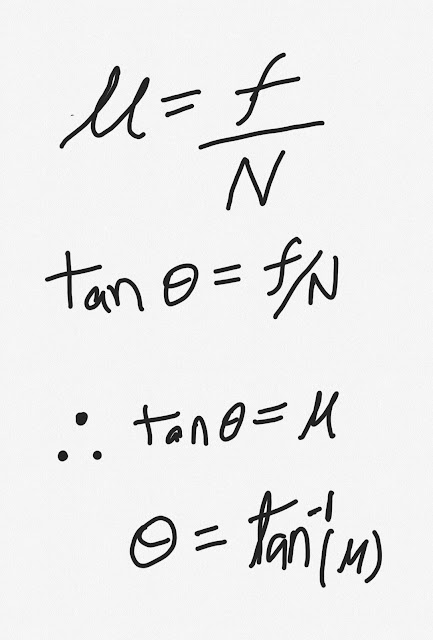
Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts or suggestions please kindly share.